Learn more about the documents detailing the progress made in the drafting of the POT for Bogotá
The Zoning Plan
-
The Zoning Plan (POT) for Bogotá, a city with 7.9 million inhabitants, is drafted and adopted
The Zoning Plan is a technical and regulatory instrument used to organize the municipal or city territory. According to Law 388 of 1997, it is the set of goals, guidelines, policies, strategies, programs, actions and norms aimed at directing and managing the physical development as well as the land use in the territory. Thus, the POT becomes a road map for the organization of urban and rural areas, in order to consolidate a coherent city-model in the long term. To this end, a series of mechanisms and instruments are devised and implemented, which contribute to its development.
What purpose does it serve?
The Zoning Plan is useful to direct and prioritize investments in the territory both by the public as well as the private sector. That is, it defines determines where parks, schools and hospitals are to be built, as well as housing, offices, commercial and industrial sites.
How are these instruments classified?
- Zoning plans: they are drafted and adopted by the authorities of population centers (municipalities and cities) with over 100.000 residents.
- Basic Zoning Plans: they are drafted and adopted by the authorities of population centers with 30.000 - 100.000 residents.
- Zoning Plan Outline: they are drafted and adopted by the authorities of population centers with less than 30.000 residents.
What are their contents?
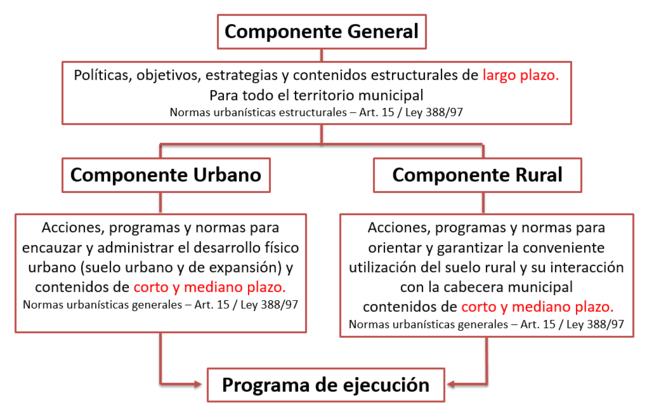
- General component: it determines the structural, long-term (12 years) contents for the municipality. The structural content refers to: environmental preservation and conservation, threat and risk areas, urbanistic, architectural and archaeological heritage, land classification as urban, rural or expansion, among others.
- Urban component: lists which actions need to be undertaken in order to manage physical urban development (urban and expansion areas) and short- and medium-term (8 years) contents. It refers to: Urbanistic norms, treatment and urbanistic actions, occupation and land uses, road infrastructure and utilities, equipment, housing, management and financing instruments, among others.
- Execution program: actions on the territory defined in the POT, to be executed during the period that the present municipal administration is in office (4 years, 8 years y 12 years).
The POT or Zoning Plan defines the urbanistic norms which regulate land use, occupation and leveraging. These norms are prioritized into a hierarchy by Law 388 of 1997, as follows:
-
Structural urbanistic norms They assure the achievement of the goals and strategies adopted under the plan's general component and under the medium-term policies and strategies in the urban component.
-
General urbanistic norms They allow for the establishment of land uses and their intensity, as well as actions, treatments and lotting, urbanization, construction procedures, as well as the incorporation into development of the different areas comprised within the urban perimeter and the expansion land areas.
-
Complementary norms They are related to the actions, programs and projects adopted during the course of the assumptions and dispositions included in the general and urban components of the Zoning Plan, and which must be incorporated into the Execution Program.
Bogotá has organized its territory under three different structures:
-
The main ecological structure Comprised by the system of protected areas, forestry reserves, urban parks, eco-parks and special handling areas, among others.
-
The functional and services structure Comprised by the mobility, urban equipment (health, education, cultural, citizen safety), public utilities (waterworks, sewage works, power, telecommunications and natural gas), and public spaces systems, in order to ensure compliance with the functions and duties provided by the elements of the socio-economic and spatial structure.
-
The socio-economic and spatial structure Comprised by the center and the network of central features concentrating economic and services activities, ensuring the urban and rural balance in the provision of services, social cohesion, Bogotá's integration at different levels, and economic development for all residents in the City-Region.